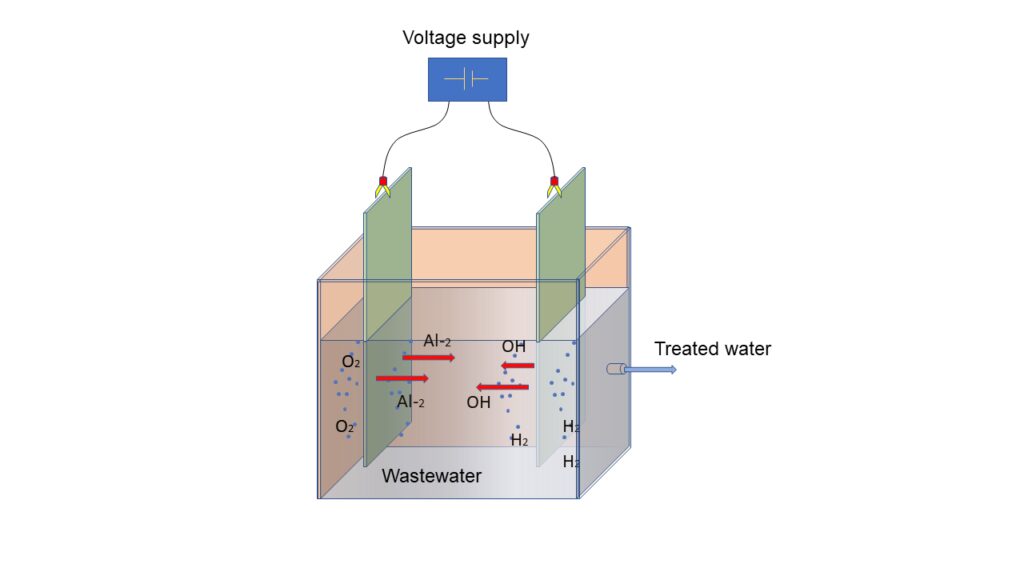
A technology applied in the treatment of wastewater, which utilizes the destabilization of dissolved, suspended, or emulsified contaminants in the water, and is achieved by introducing an electric current into the water through parallel metal plates of various materials, the most common being iron and aluminum.
Following this process, on one side, an effluent with a high iron or aluminum content is produced, which must be treated with other technologies, and on the other side, a series of sludges that are subsequently separated using traditional methods (filtration, decantation, or flotation).