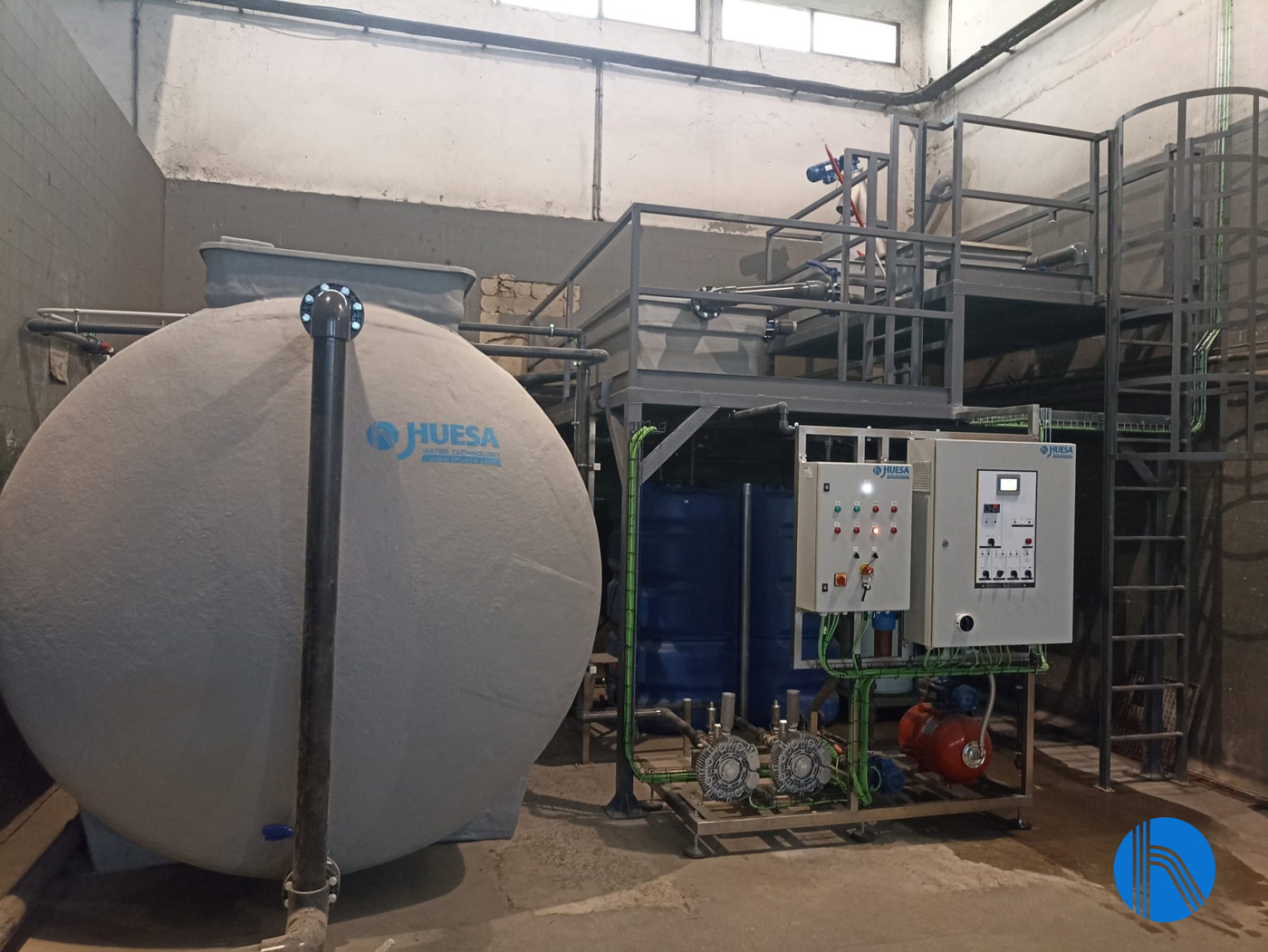
We share with you a new success story for a company dedicated to waste collection in one of the main Spanish cities. Our client, a leading company in its sector, needed to reuse water from its activity to reduce the consumption of this resource as part of its commitment to sustainable development.
After studying our client’s needs, J. Huesa‘s technical team opted for the design and manufacture of a tailor-made effluent treatment plant using MBR followed by a chlorination and accumulation system for use in the washing of its fleet of vehicles.
Background and design data
Design capacity
The plant has been designed to guarantee the treatment of 2 m3/day; the installation has been designed to treat wastewater from our client’s staff toilets and changing rooms, as well as from the washing of trucks, resulting in the composition of the raw water as follows:
- BOD5 ≤ 400ppm
- COD ≤ 600ppm
- SS ≤ 450ppm
- TN ≤60ppm
Treated water requirements
The expected performance of the equipment for the maximum parameters indicated above is as follows:
- BOD5: 96% reduction
- COD: 90% reduction
- Suspended solids: 96% reduction
- Escherechia Coli < 200 CFU/ 100 ml (Performance achieved thanks to the molecular cut of the ultrafiltration membranes that remove viruses and bacteria, and the subsequent continuous chlorination of the treated water tank, which will ensure that a residual free chlorine value is maintained in the water).
Since water reuse is regulated by RD 1620/2007, which establishes water quality criteria according to the use to be made of the reused water, being for the case of truck cleaning the following quality:
The supplied equipment consists of a series of equipment with the aim of complying with the RD for water reuse, in which the water permeate is obtained with the following characteristics:
| pH | 6,5 -10 |
| COB5 | < 1.000 mg/L |
| COD | < 1.750 mg/L |
| SS | < 1.000 mg/L |
| Oils and Fats | < 100 mg/L |
| Conductivity | < 7.500 mg/L |
| Total hidrocarbons | < 20 mg/L |
| Iron | < 10 mg/L |
Table 1. Characteristics of treated water
Solution adopted
After studying the starting conditions and the general objectives of the project, J. Huesa‘s technical team opted for the design, tailor-made manufacturing and supply of a water treatment plant composed of the following treatment train:
- Pretreatment
- MBR
- Continuous chlorination and accumulation system
Pretreatment
The water enters the installation directly driven by a submersible pump, feeding a vertical screw screen made of ASI304 stainless steel and coupled in the GRP tank. It is operated by the plant’s general electrical panel and works automatically following a programming scheme that raises the solids by means of a screw that deposits them in a collection container. In parallel, a manual bar screen is integrated as a safety element in case of screw screen failure, with a 20 mm pitch that aims to retain and separate large floating and suspended bodies dragged by the wastewater. It is made of polyester reinforced with fiberglass and is supplied together with a solids collection basket.
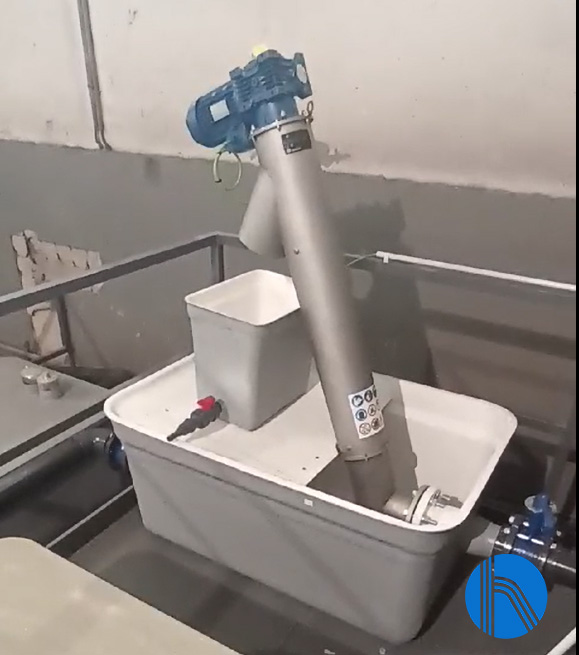 Image 1. Screw conveyor detail
Image 1. Screw conveyor detail
The screw is equipped with a timer that is programmed according to the amount of solids contained in the water.
The main component of the pretreatment is the hydrocarbon separator, which is a grit and grease separator whose function is the physical separation, by density difference, of fats and oils of vegetable and animal origin, while promoting the settling of larger solids.
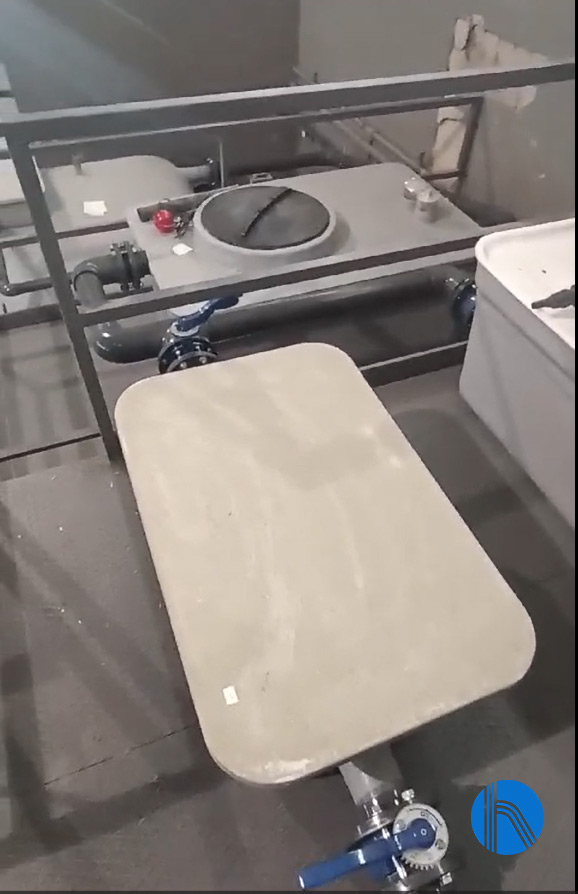 Image 2. Bar screen and HC separator detail
Image 2. Bar screen and HC separator detail
The separation of fats provides a very significant increase in the performance of the secondary treatment (MBR) since if they were combined with organic matter, they would prevent its degradation by reducing the transfer coefficient. In addition, fats increase the amount of BOD5 at the outlet of the treatment plant.
In addition, the last chamber of this equipment will function as an anoxic reactor prior to the biological reactor so that, together with the biological reactor, Nitrification-Denitrification for the elimination of Nitrogen can take place.
The water is separated from the grease, thanks to the difference in densities causing the separation of the liquid into two phases: the upper phase with a higher content of grease and the water in the lower area.
MBR
In the biological reactor, the different reactions that are necessary for the biochemical decomposition of organic matter take place. For these to take place, an oxygen supply is required to provide aerobic conditions in the reactor and to keep the microorganisms responsible for degradation in suspension.
Unlike conventional extended oxidation, the reactor operates with higher solid concentrations so that greater oxygenation is required, and with higher sludge age, resulting in higher purification efficiencies.
The membranes installed in the reactor perform the solid-liquid separation by filtration. By means of a suction system (mono helical pump), a vacuum pressure is exerted on the membranes creating an outside-in flow so that the water penetrates through the membranes, leaving the solids and bacteria retained on the outer wall.
The diffusers installed under the membranes and the blowers installed on the outside allow the generation of an ascending air bubble flow that allows cleaning of the outer wall surface of the membranes, as well as oxygenating the bioreactor.
The extended aeration system operates with a reduced mass load and a high sludge age which, together with the high retention time, allows the elimination of carbonaceous organic matter and nitrification of the effluent.
Chlorination – accumulation system
The effluent water from the MBR system is accumulated in a 3,000-liter tank, from which a recirculation-chlorination system is implemented. From this tank, the water is passed through a circuit in which sodium hypochlorite is dosed thanks to a continuous measurement of free chlorine in the chlorination system, implementing a PID loop with the dosing pump, with the objective of maintaining the accumulated water with the necessary conditions for its reuse according to Royal Decree 1620/2007 for the use of water in industrial use.
From this treated water tank, a connection will be made to a pressure group prepared so that the client can connect to the treated water and allow the washing of trucks.
Instrumentation and control
The plant is equipped with instrumentation and control elements (automatic valves, pressure switches, pressure transmitters, flow meters, conductivity and Redox meters, among others) that are centralized in an electrical panel.
The panel also includes a programmable logic controller and a touch screen for the operation and configuration of the plant. The Instrumentation and Control team at J. Huesa has designed the control panel to be integrated into the client’s SCADA system, allowing personalized programming of all operating parameters, as well as external connections for levels, alarms, pretreatment, among others, through different I/O modules.
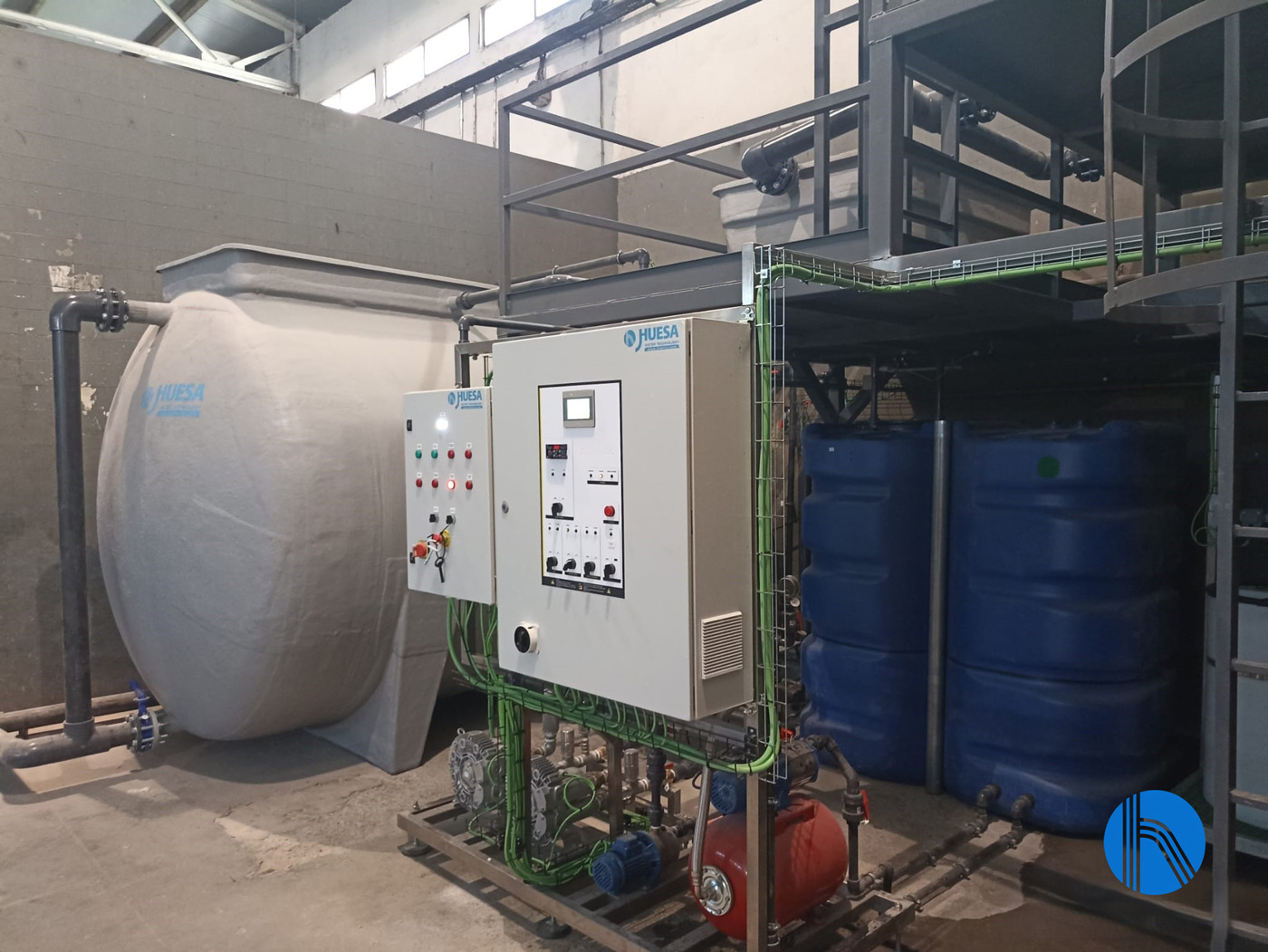 Image 3. CE view in the installation
Image 3. CE view in the installation