In an increasingly digital world, data centres are critical infrastructures for storing and processing information. Cooling is essential to their operation, and water plays a key role in cooling systems. However, the quality of the water used has a direct impact on the efficiency, maintenance and sustainability of these systems. In this article, we explore the importance of water in data centres, the challenges associated with its use, and how advanced technologies are optimising its management.
The role of water in data centre cooling
Water cooling systems are widely used in data centres due to their thermal efficiency and lower energy consumption compared to air-based alternatives. There are various configurations, such as cooling towers and closed-loop systems, which rely on water quality for proper operation.
Data centre cooling systems can be configured as open or closed loop systems, each with their own water management and treatment requirements:
- Open circuits: These systems, such as cooling towers, remove heat by evaporation of water, which causes a progressive concentration of salts and other contaminants. Because of this constant evaporation, it is necessary to continuously replenish water and apply treatments to prevent scaling, corrosion and microbiological growth.
- Closed circuits: In these systems, water circulates in a closed loop without direct contact with the environment, minimising evaporation and the ingress of external contaminants. While this approach significantly reduces the need for water replenishment, it is essential to maintain strict quality parameters to avoid corrosion and mineral deposits.
Understanding these differences allows us to select the most appropriate treatment strategies for each type of system, ensuring efficient and sustainable use of water in data centre cooling.
At J. Huesa we design, manufacture and implement customised water treatment solutions for data centres, guaranteeing quality, efficiency and sustainability.
Key water quality parameters
To maintain the efficiency of cooling systems, it is essential to monitor and control certain water parameters:
- pH: Should be maintained within a range that prevents corrosion and scale formation.
- Conductivity: Indicates the amount of dissolved solids; high levels can indicate a risk of corrosion.
- Hardness: Reflects the concentration of calcium and magnesium ions; high hardness can cause mineral deposits.
- Alkalinity: Influences the water’s ability to neutralise acids and can affect scale formation.
- Oxygen content: High levels can accelerate corrosion of metal components.
- Presence of micro-organisms: It is essential to control bacterial growth to avoid problems such as legionellosis.
Challenges in the use of water in data centres
The continuous use of water in these systems presents technical challenges that affect both the performance and longevity of equipment:
- Corrosion: Occurs when water contains dissolved oxygen or has an inadequate pH, accelerating the deterioration of pipes and equipment.
- Scale: The presence of calcium and magnesium salts promotes the formation of deposits that reduce thermal efficiency.
- Microbiological growth: In open systems, the proliferation of bacteria and algae can clog pipes and affect heat exchange.
To mitigate these problems, it is essential to implement adequate water treatment to ensure optimal parameters of conductivity, hardness and microbiological content.
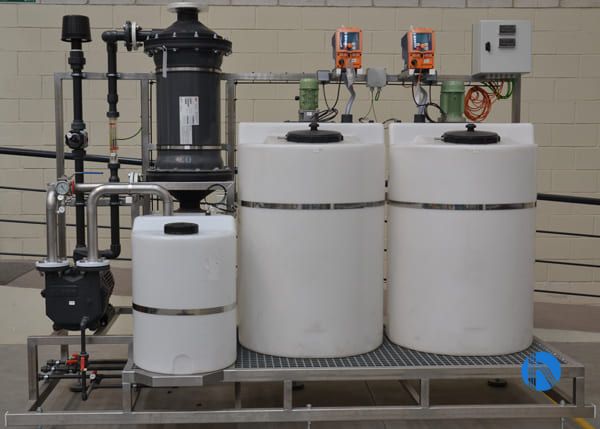
Data centre water treatment technologies
The main water treatment technologies used in these systems and their benefits are outlined below.
1. Filtration

Mechanical filtration uses screens, cartridges or sand beds to retain suspended particles and solids carried by make-up water.
Benefits:
- Prevents sediment build-up in pipes and equipment.
- Reduces the load of contaminants that can promote biological growth.
- Improves thermal efficiency by preventing clogging of heat exchangers.
2. Ion Exchange softeners
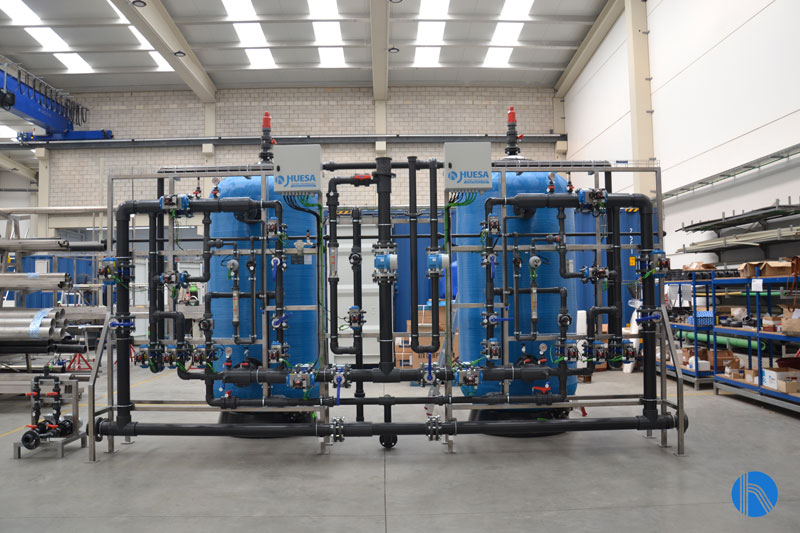

Softeners exchange calcium and magnesium ions for sodium, reducing water hardness and preventing limescale.
Benefits:
- Reduces calcium carbonate deposits in equipment.
- Improves heat exchanger efficiency and reduces energy consumption.
- Reduces the need for chemical cleaning and corrective maintenance.
3. Nanofiltration and reverse osmosis
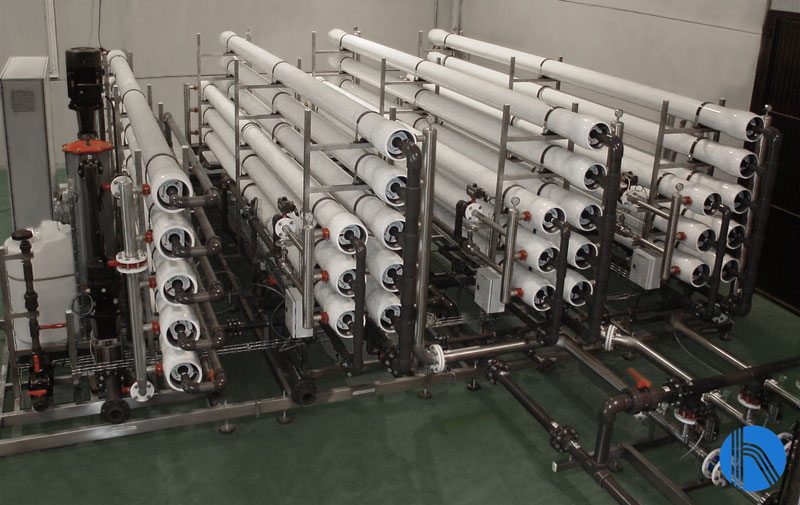

Both technologies use semi-permeable membranes to remove salts, particles and organic contaminants. Nanofiltration is less pressurised and selectively removes hardness and organic matter, while reverse osmosis removes up to 99% of dissolved solids.
Benefits:
- Allows precise control of feed water quality.
- Reduces corrosion and scaling by removing salts responsible for scale formation.
- Reduces microbiological growth by removing organic contaminants.
4. Chemical treatment (corrosion and fouling inhibitors)
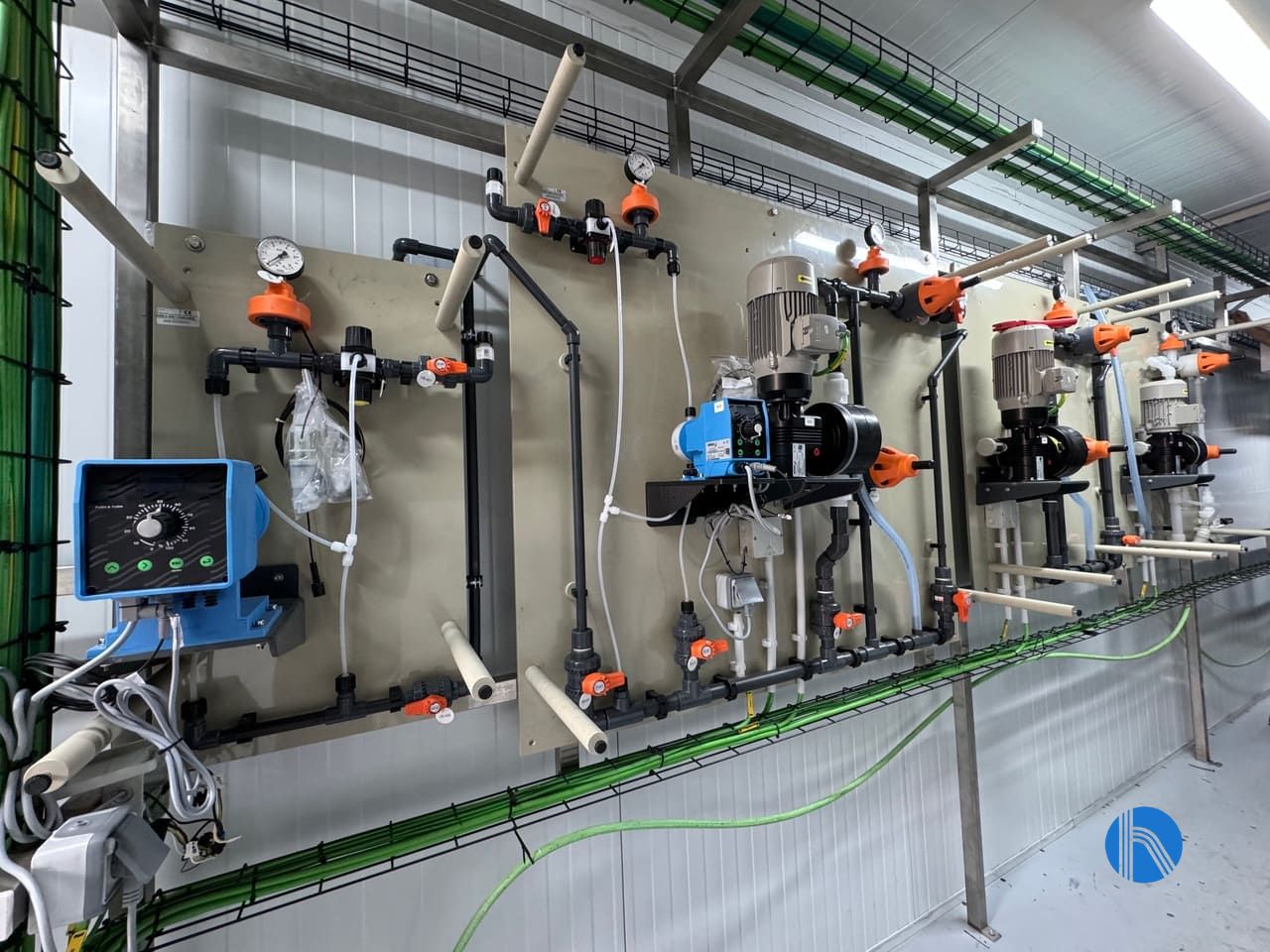

The use of specific chemicals helps to control corrosion, scale and microbiological growth.
Benefits:
- Protects metal surfaces from chemical attack.
- Maintains the chemical balance of the water in the closed circuit.
- Allows for more stable operation with less frequent cleaning.
5. Degassing and dissolved oxygen control

Dissolved oxygen in water is a key factor in the corrosion of cooling systems. Technologies such as thermal deaeration or the use of deoxygenating products eliminate this problem.
Benefits:
- Reduces corrosion of piping and metal equipment.
- Increases system life by minimising wear on materials.
- Improves operating efficiency by maintaining an oxygen-free environment.
6. UV radiation treatment
The UV disinfection system inactivates micro-organisms in the water without the addition of chemicals.
Benefits:
- Eliminates bacteria and algae without creating harmful by-products.
- Reduces the need for chemical biocides.
- Maintains water quality without
Each of these technologies for water treatment in closed cooling circuits offers specific advantages that can be combined according to the needs of the system. The correct selection and implementation of these solutions can optimise thermal efficiency, reduce operating costs and ensure the sustainability of water use in industrial and technological environments.
However, choosing the right technology depends not only on the characteristics of the cooling circuit, but also on water treatment expertise. Having a company that specialises in designing bespoke solutions is key to ensuring that the strategy adopted is optimal in terms of efficiency, durability and sustainability.
Experience in water analysis, risk assessment and implementation of advanced technologies allows these companies to offer solutions tailored to each system, minimising operational problems and maximising equipment performance. In this context, technical know-how and innovation in water treatment play a decisive role in the reliability and competitiveness of industrial processes.
Case study: Application of nanofiltration in a data centre
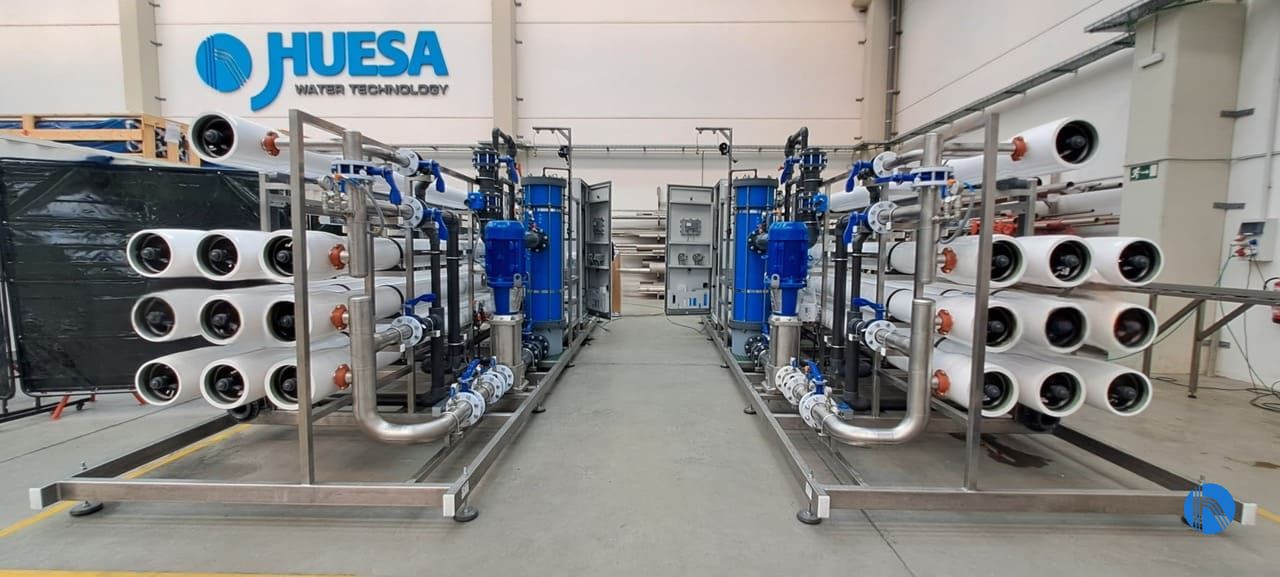

J. Huesa, a company specialising in water treatment solutions for industrial applications, recently installed a nanofiltration system in an important data centre in Spain.
- Initial situation:
The customer needed to adapt the mains water to the quality of a closed cooling circuit.
- Solution implemented:
Two nanofiltration water treatment units, each with a flow rate of 57 m3/h, which made it possible to adapt the characteristics of the feed water by selectively removing the salts responsible for scaling, without compromising the quality of the cooling water.
- Results obtained:
- 75% reduction in the formation of mineral deposits, improving thermal efficiency.
- Lower consumption of chemical products, reducing environmental impact.
- Increased equipment life, reducing operating costs.
Conclusion:
Water is an essential resource in data centre cooling, but its quality must be properly managed to avoid technical problems and ensure efficient operation. Technologies such as nanofiltration offer an advanced and sustainable solution to optimise water use in these critical environments.
J. Huesa specialises in providing innovative solutions for water treatment in industrial processes, ensuring operational efficiency and sustainability in strategic infrastructures such as data centres.
If your data centre needs to optimise its cooling system, contact our experts to analyse your case and design the right solution.