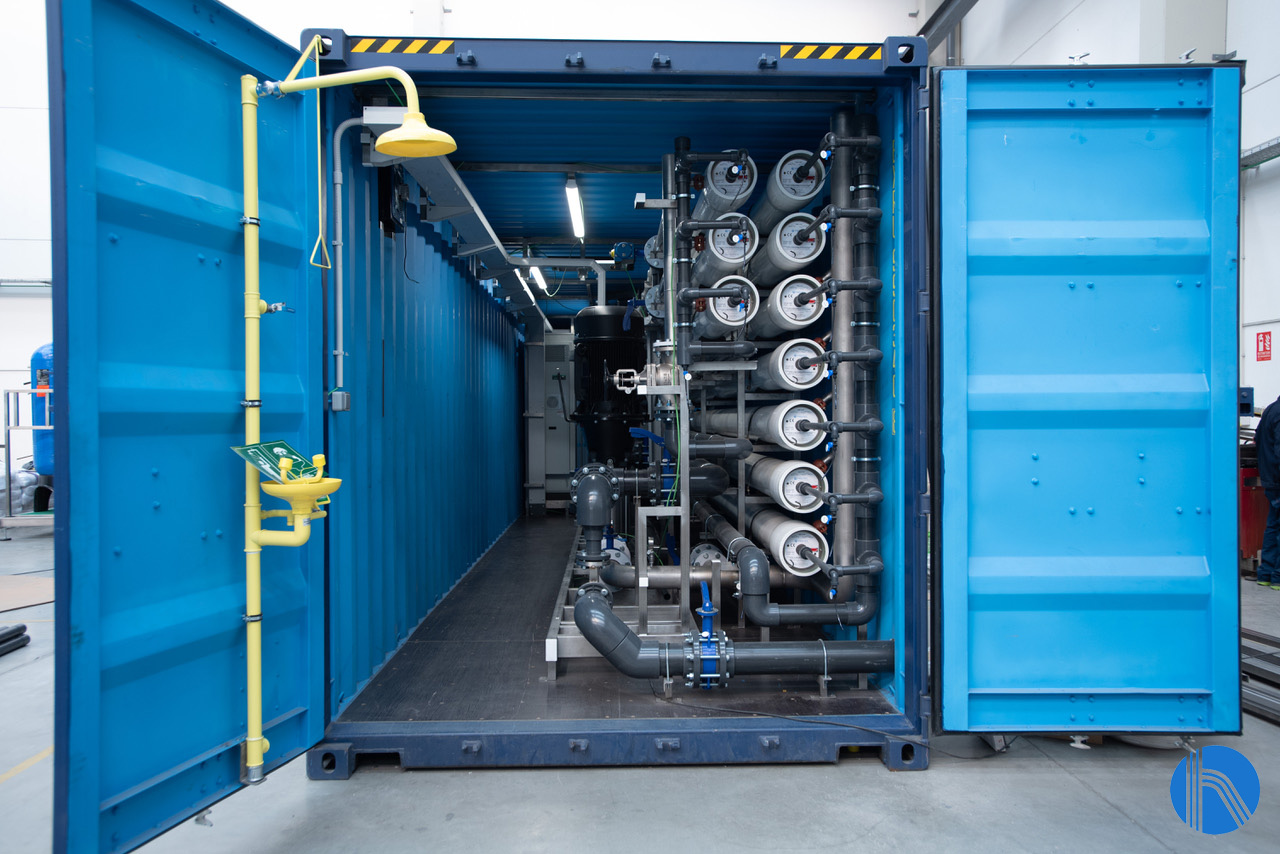
We share with you a new successful project done by J. Huesa Water Technology, consisting of the execution of a containerised treatment plant to reuse water from a MBR of an agri-food industry located in Latin America.
Once the analytical parameters of the raw water and the requirements of our client were known, the technical team of J. Huesa studied and designed of a containerised solution.
The purpose of the water treatment plant is to establish a solution to reuse water from the MBR installed in the factory.
The starting data are as follows
Adopted solution
Considering the physical and chemical characteristics of the water, the design of a containerised reverse osmosis plant, including the following sub-processes, was chosen:
-
Pre-treatment
In a first stage, the water coming from the MBR is dosed with an anti-scaling – dispersing product. It prevents the salts present in the feed water (calcium and magnesium, sulphates, silica, among others) from fouling the membranes and, therefore, loss of treated water flow. This is done continuously while the plant is in operation.
Subsequently, a non-oxidising biocide agent is dosed to eliminate the proliferation of organic contamination present in the water
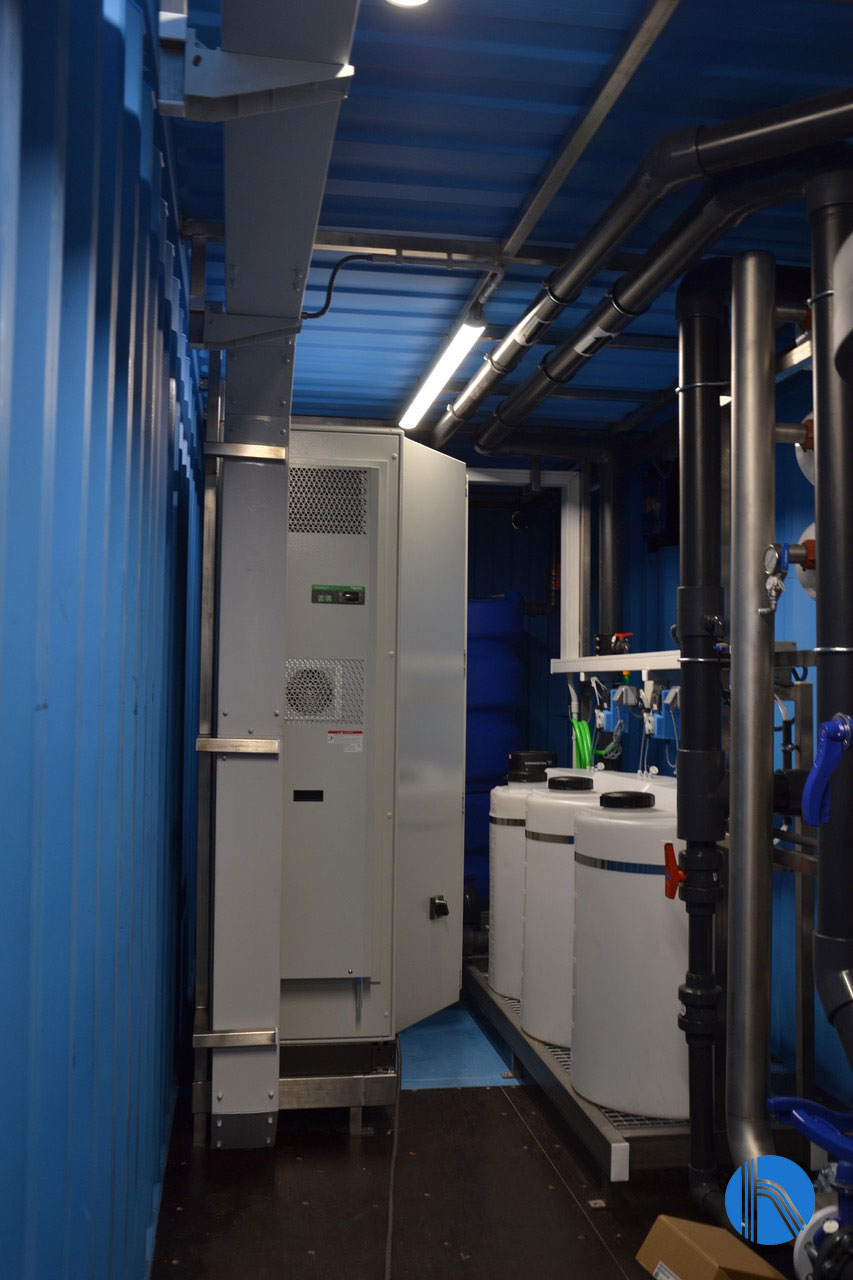

Detail of dosing tanks
-
Reverse Osmosis System
The pre-treated water passes to the reverse osmosis module, where it circulates through a 5-micron pore size safety pre-filter in which any colloids and suspended solids that may have escaped from the MBR are retained.
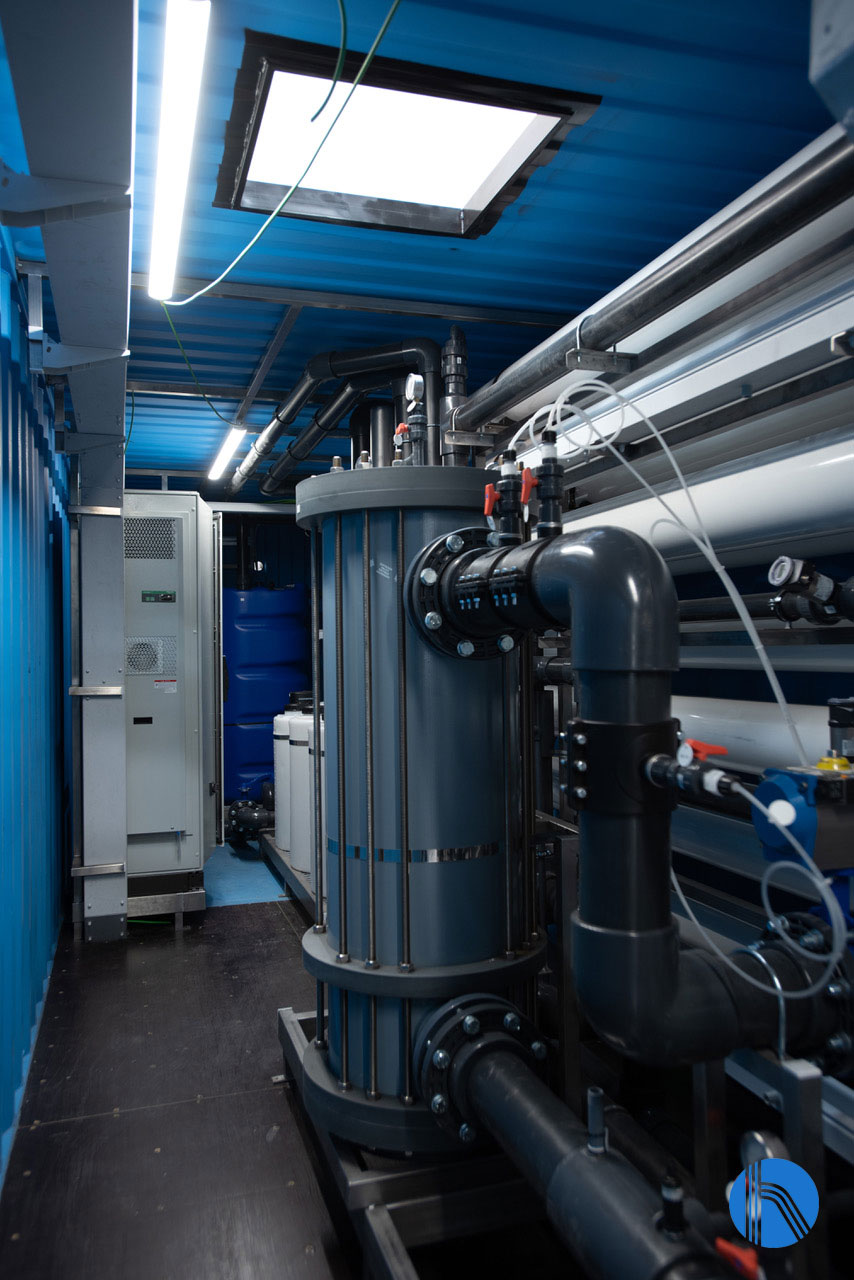

Detail of the safety pre-filter
Then, the water is pumped to the reverse osmosis system by means of a high-pressure vertical pump made of AISI 316 stainless steel, which guarantees the operating pressure and allows the production flow rate required in the case in question to be obtained. Its function is to maintain a constant inlet pressure to the osmosis system, using a control loop consisting of a pressure transmitter and frequency variator.
The reverse osmosis system is designed for an input flow of 75 m3/h and has a conversion factor of 70 %. The plant is equipped with spiral wound membranes, made of polyamide, and specially designed for brackish water up to 8000 ppm and for working at low pressure. They are mounted in pressure housings, made of GRP.
These membranes have a free chlorine tolerance of 0.1 ppm and a maximum operating pressure of 41 bar
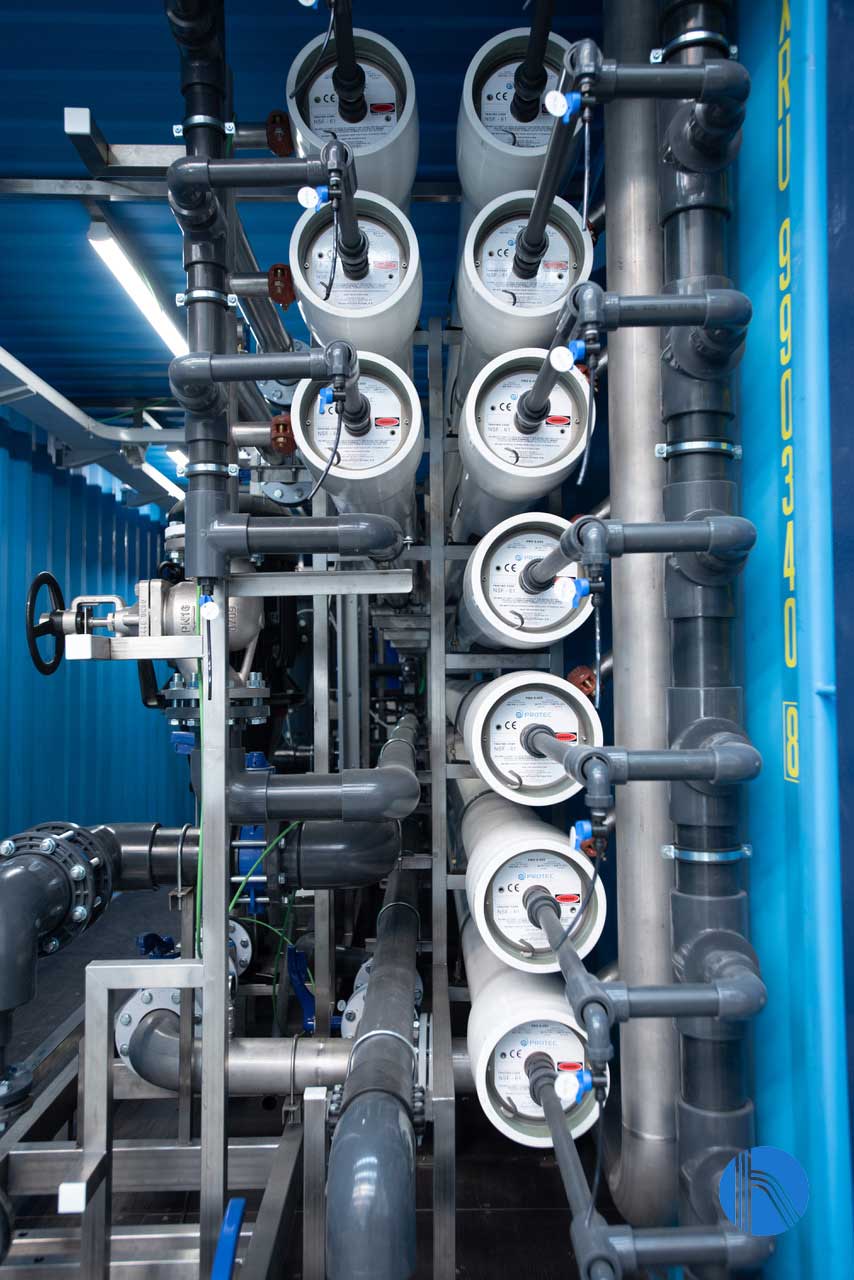

Detail of reverse osmosis housings
These membranes have a high chemical resistance, as they can operate in a pH range of 2 to 13, which makes them very easy to wash and recover, as they accept a wide variety of washing chemicals.
For monovalent ions, the separation selectivity varies between 90 and 95 %. For divalent ions the selectivity is over 98 % and for mineral or organic colloids, bacteria, and viruses, this selectivity reaches 99,9 %.
-
Membrane cleaning system
A flushing system has been installed in the reverse osmosis skid to ensure automatic cleaning of the membranes inside the tube. In this case, the system consists of a reagent preparation tank, a stainless-steel recirculation pump, and stainless-steel isolation and recirculation valves.
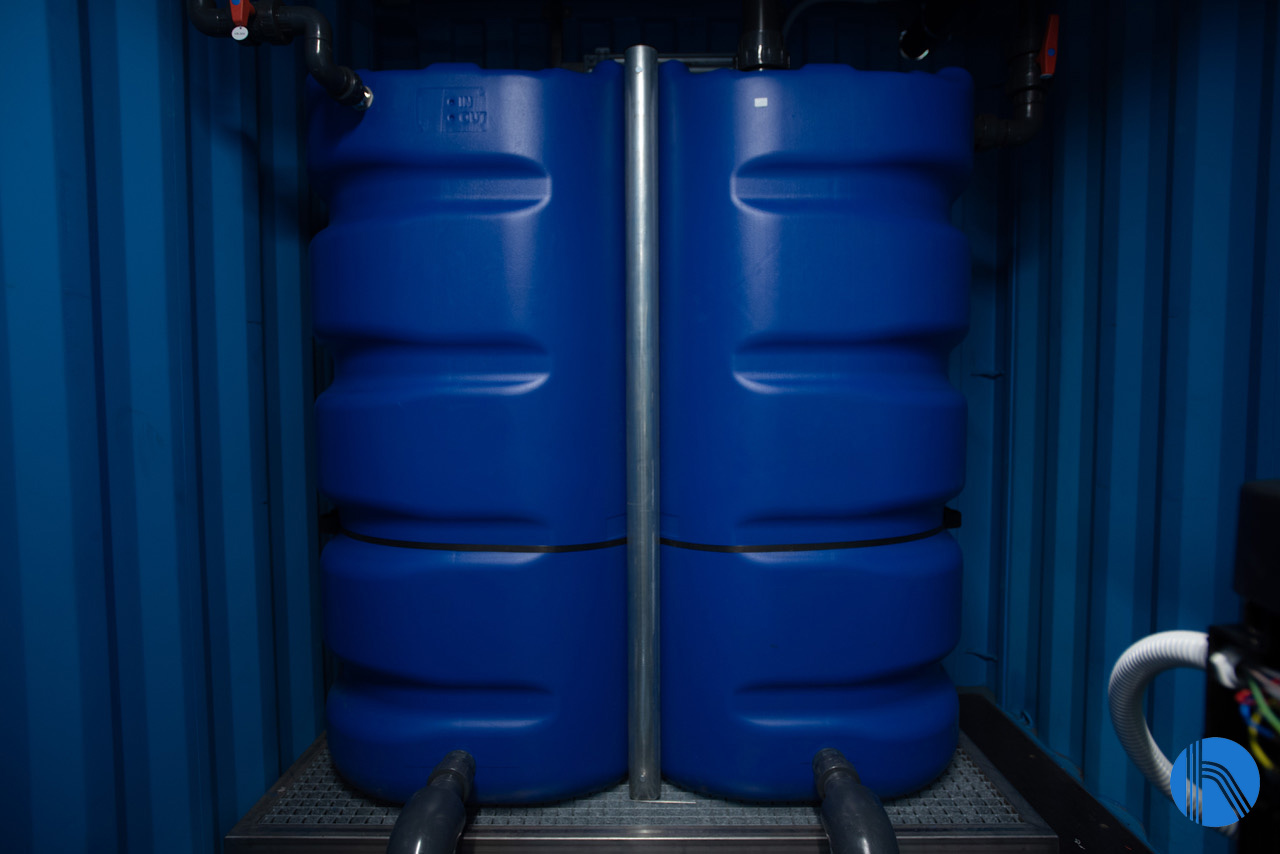

Detail of the sweep tank
-
Instrumentation and control
The reverse osmosis plant is equipped with instrumentation and control elements (automatic valves, pressure switches, pressure transmitters, flow meters, conductivity, and pH meters…) that are centralised in an electrical protection and control panel, located in the main skid.
Furthermore, the panel includes a programmable logic controller and a touch screen to monitories and control the process, and a router with Ethernet/4G connection for remote control. J. Huesa‘s Instrumentation and Control team has designed the control panel so that it can be integrated into the customer’s SCADA system.
In this way, the electrical panels that control the treatment plant are equipped with remote communication systems, so that their operation can be controlled without the need of on-site assistance.
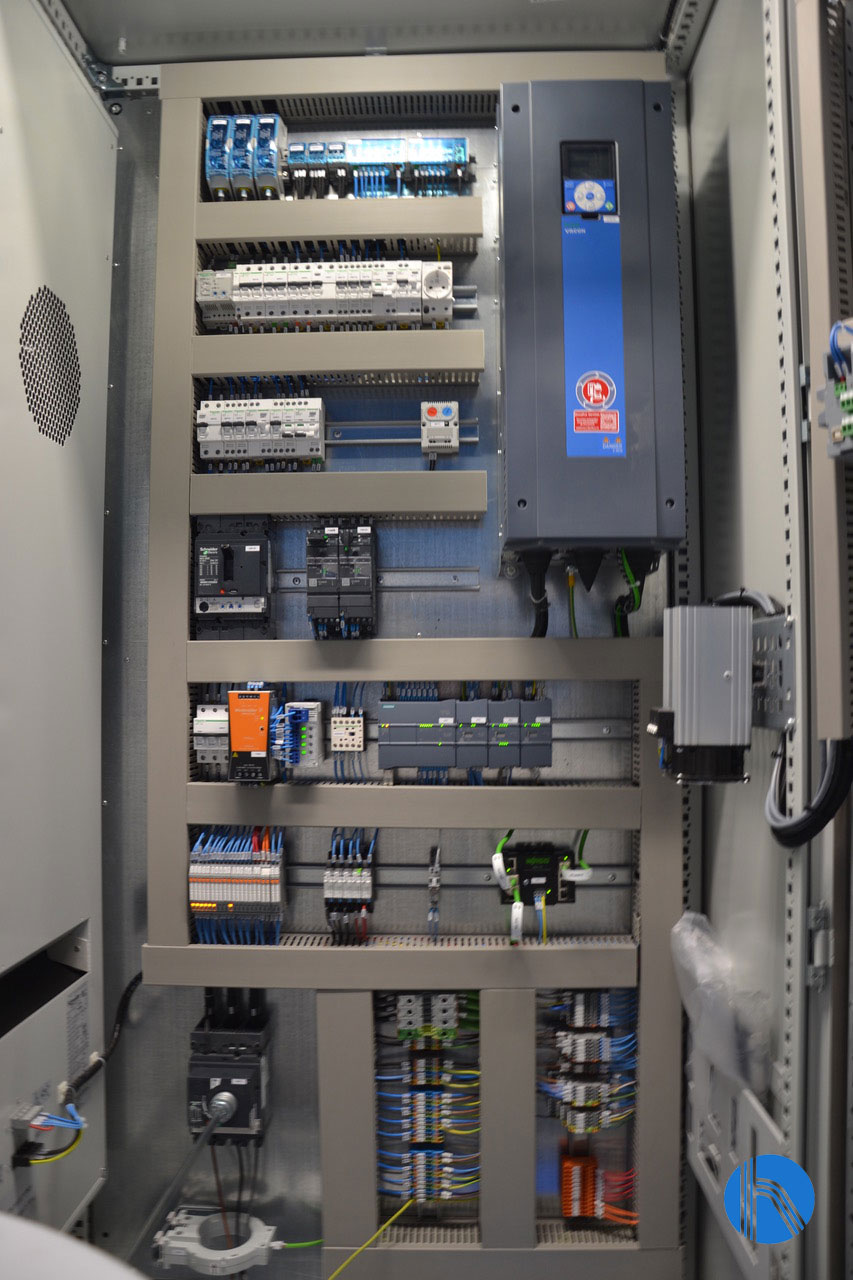

Detail of the electrical panel
With this project, J. Huesa is committed to the use of reverse osmosis technology and gives our client some additional advantages, such as:
- The system works continuously, without the need for regeneration.
- The system is fully automatic and can work up to 24 hours a day with minimum supervision.
- It provides a bacteriological barrier in the water produced by the semi-permeable nature of the membranes.
- No toxic, dangerous or environmentally polluting discharges are produced.
- Fungible products are scarce.